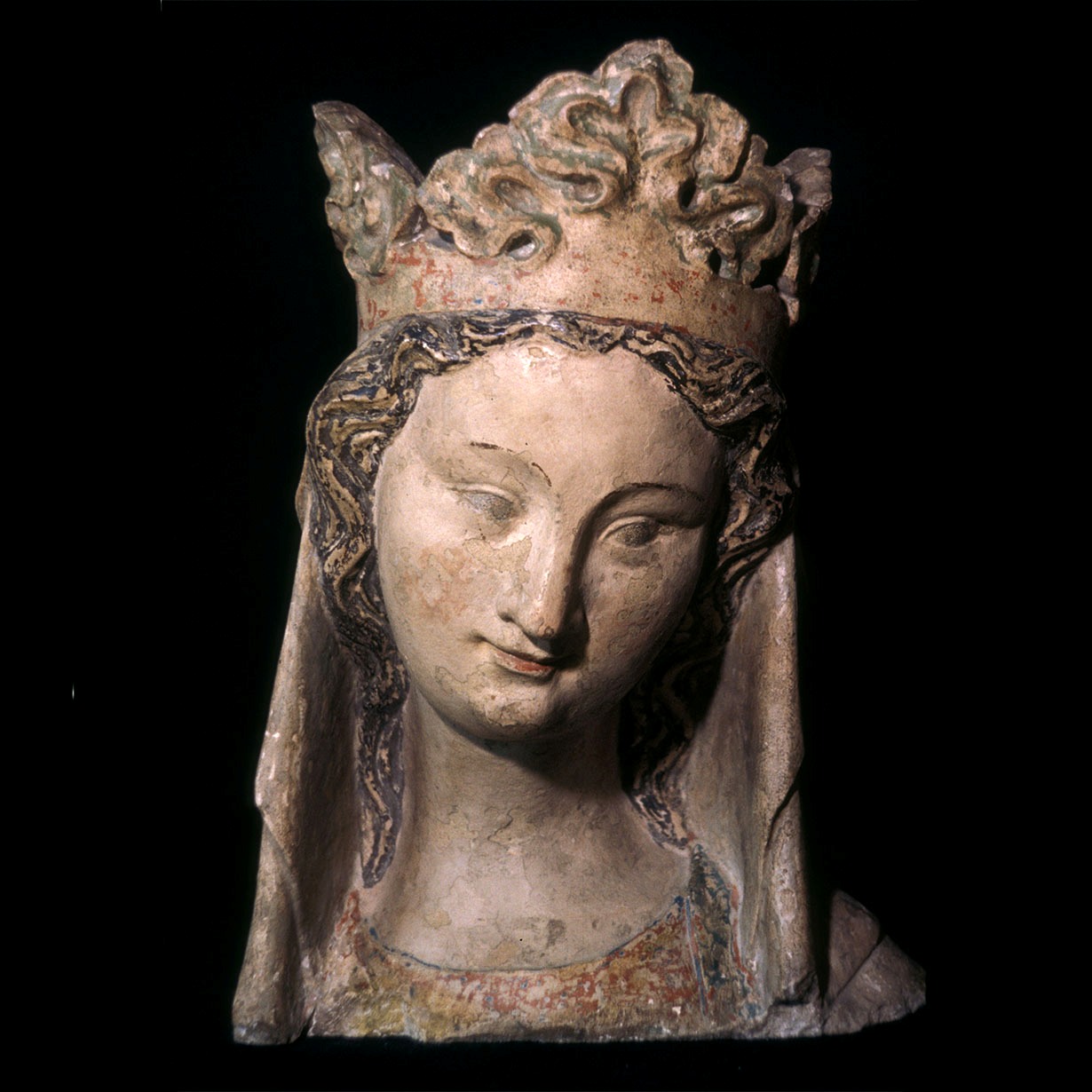
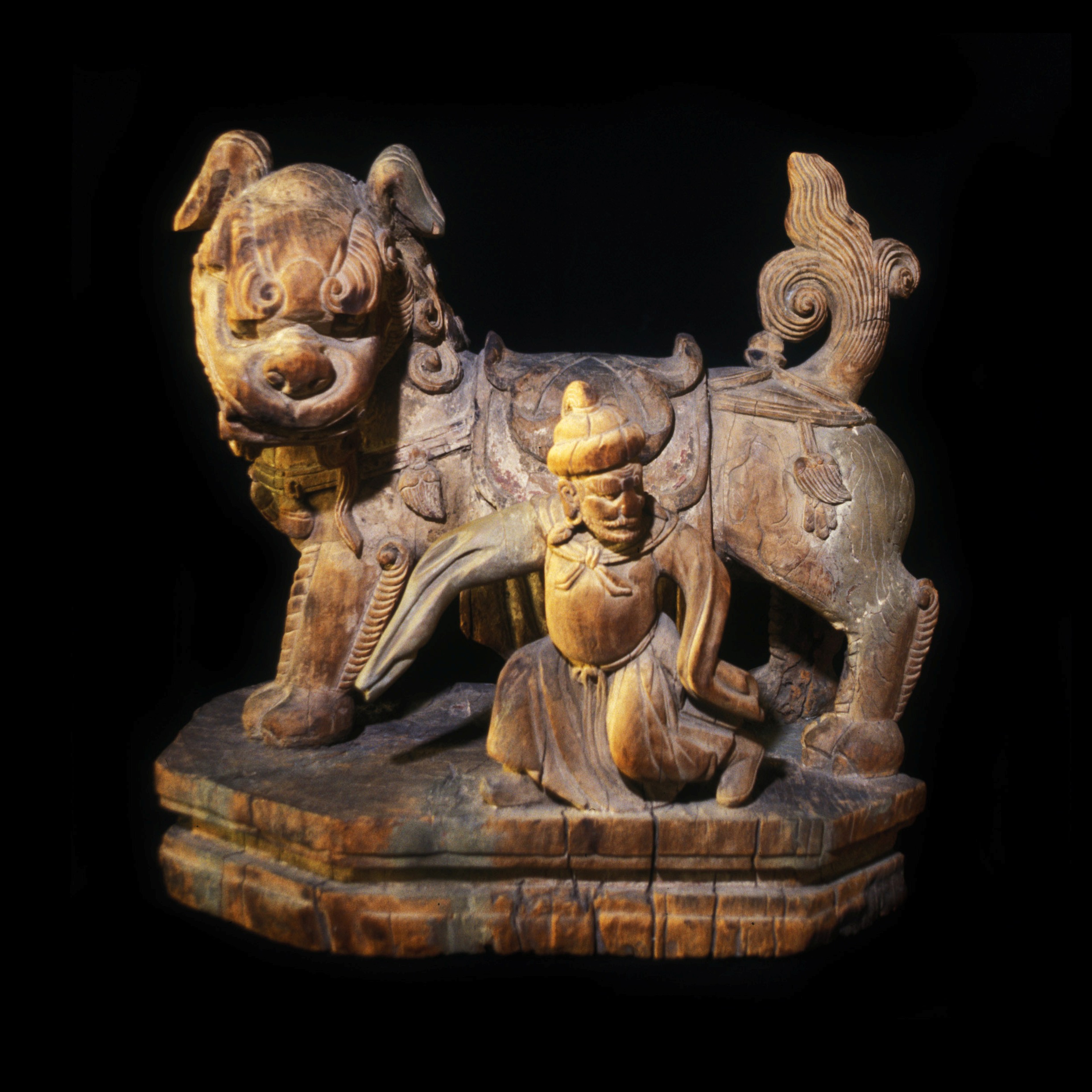
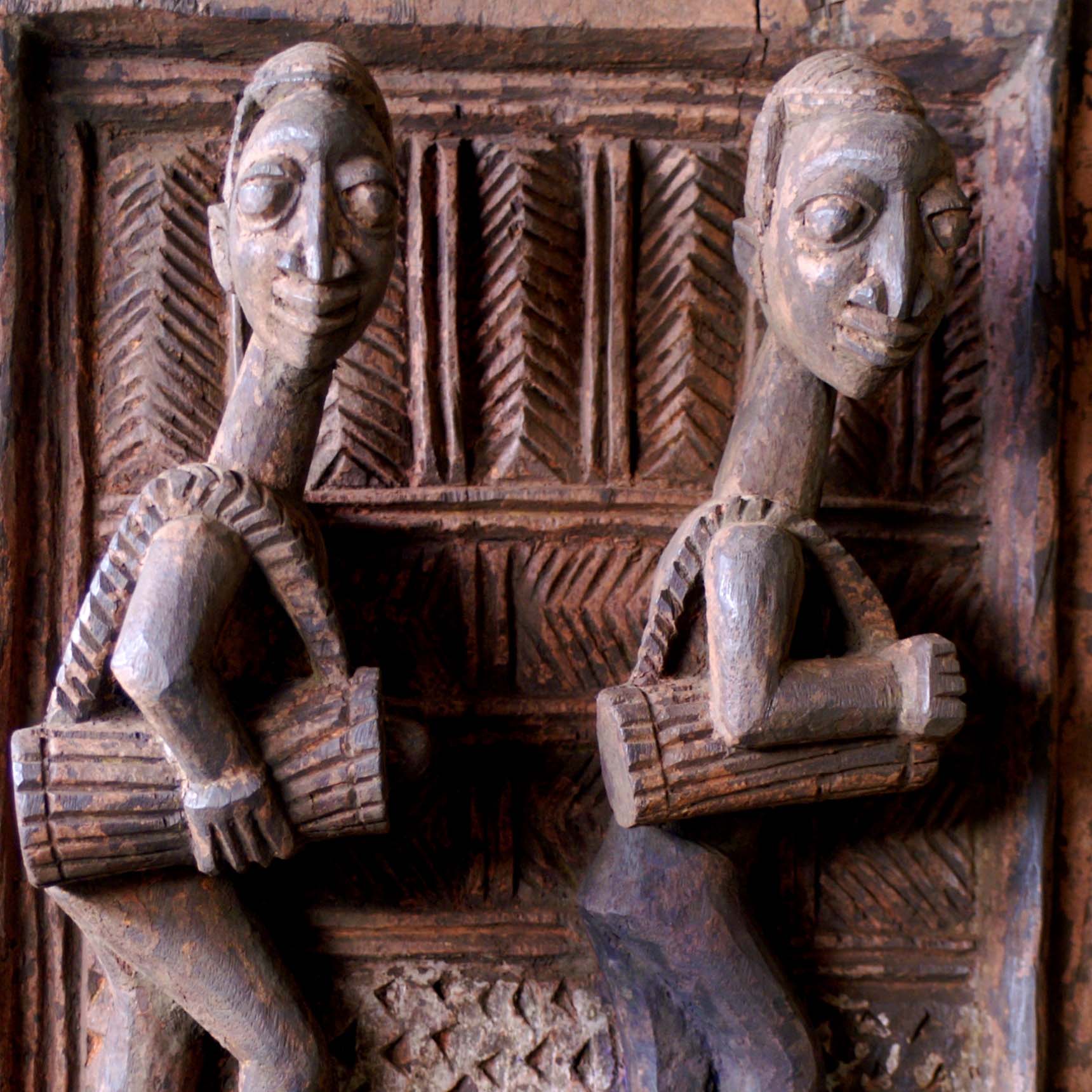
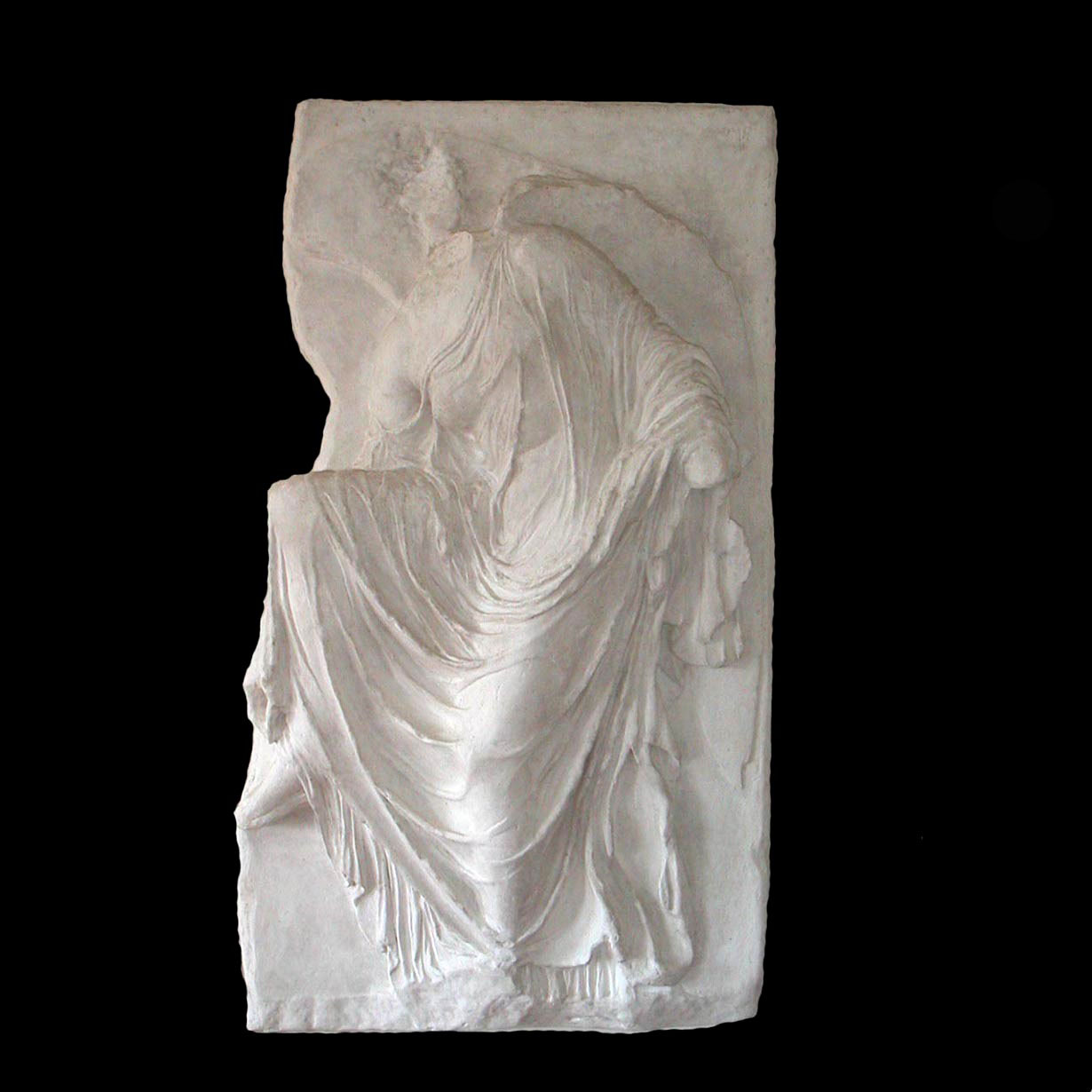
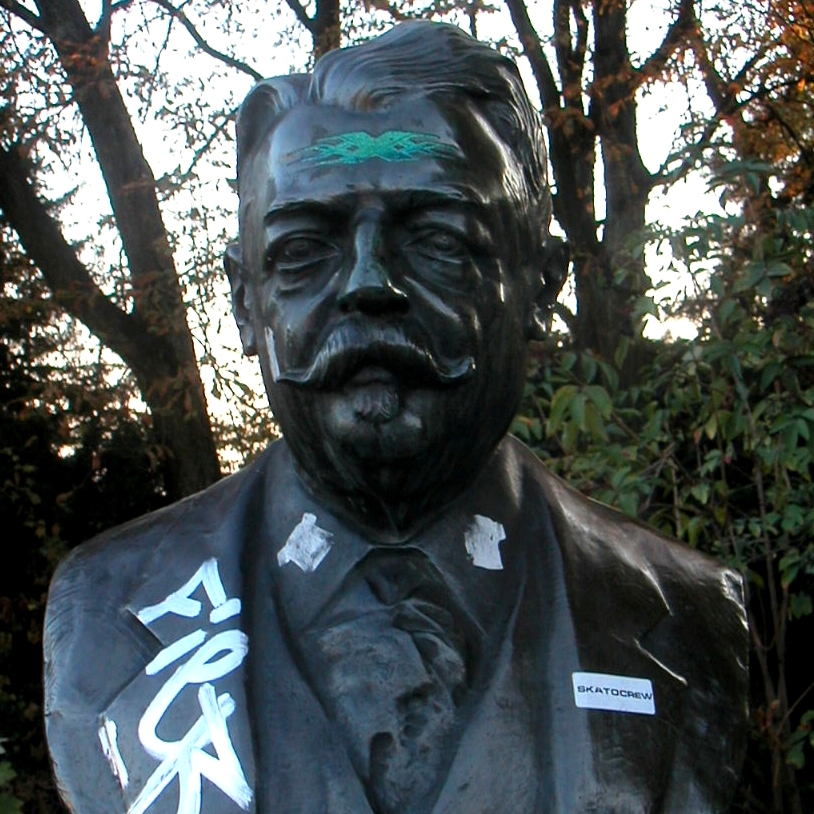Polychrome wooden Sculptures:
Frequent problems encountered with painted wooden sculptures are loose paint layers and wood worm damage.According to the size of the object insect attacks can be treated chemically or through deprivation of oxygen. For large quantities exposure to nitrogen is recommended. Loose paint layers can be consolidated and put back into place and, if necessary, the lacunae can be completed. Later repaints can be removed in order to reveal the original paint.
Plaster and Terracotta Sculptures:
With such sculptures the most frequent problem comes from surface dirt. This can be removed mechanically or chemically depending on the surface finish and condition. Fragments are re adhered with reversible adhesives, gaps filled and if necessary retouched.
Metal Sculpture:
Conservation treatments of outdoor bronze sculpture aim at stabilizing the metal and at reducing the colour contrast. Light green anodic areas are treated with air abrasive and a soft abrasive such as ground nutshell without damage to the original surface. Black crusts are removed mechanically. In order to withstand outdoor conditions protective coatings such as microcrystalline waxes are used. When dealing with wrought and cast iron, more durable coatings are necessary. After a complete removal of all corrosion products, combined protective coatings are used. These usually consist of an anodic primer, followed by epoxy or polyurethane coatings.
For metal sculptures kept indoors in a controlled environment less interventive methods are used. Surfaces are cleaned and coated with a compatible and reversible protective coating.
For both in-and outdoor sculptures a regular maintenance program is recommended to prevent extensive corrosion and costly conservation treatments.